Elimination with matrix
January 8, 2017
Hello.
In this post, I’m going to explain about elimination with matrix.
Sometimes, Elimination can be fails, but usually it’s succeeded.
Now Let’s see what I want to show.
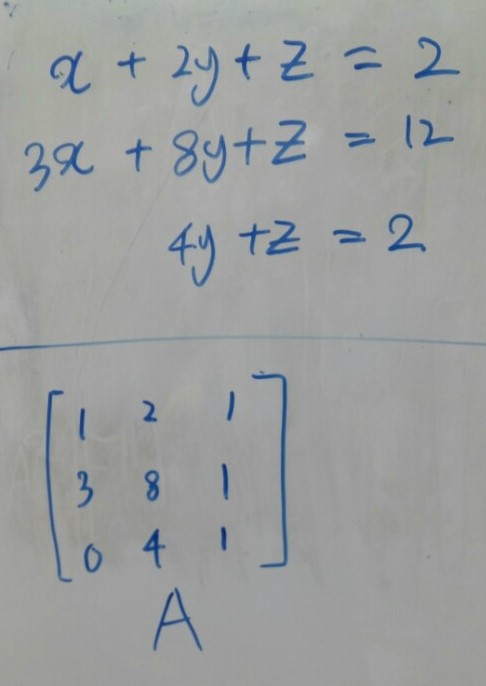
[Picture 0]
Here’s the system of equations. Three equations and three unknown.
And Here’s also a matrix 3x3. This is the system Ax=b, We’ve seen it in the last post.
The Matrix A is totally same as the equations except there’s no annoying equal signs and unknowns.
What’s the first step of elimination? What we do to solve the equations?
I’m going to subtract the first equation from the second equation with the proper numbers.
For what?, To remove the x part of the second equation.
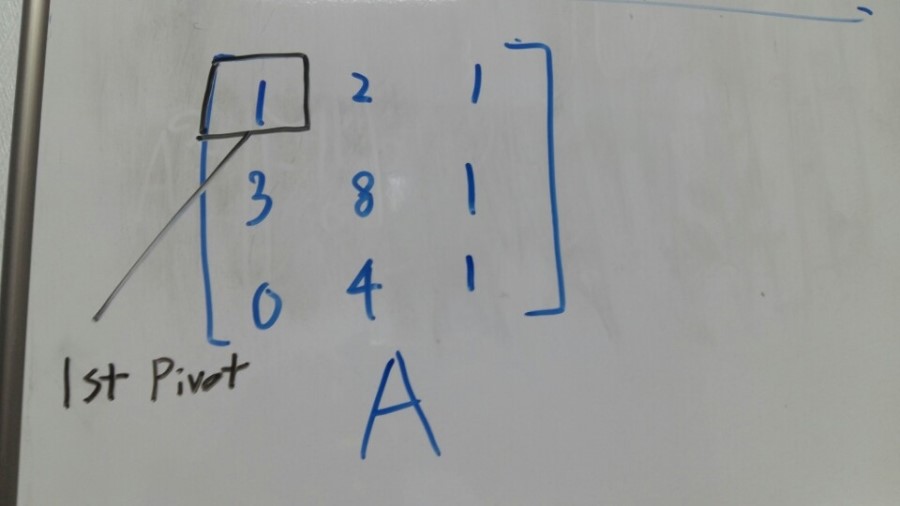
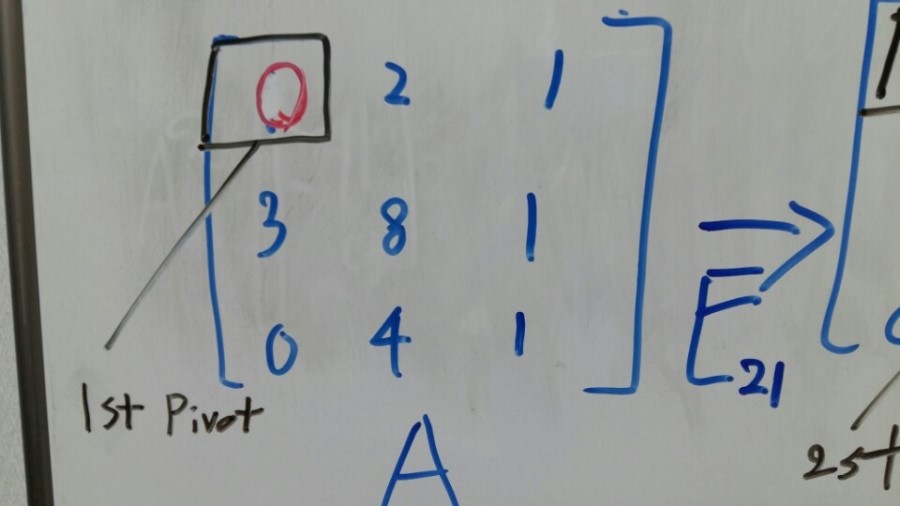
For that, which one do I have to use in the first equation?
The x part is 1. It’s called a pivot.
And I’m going to call it 1st pivot.
[Picture 1]
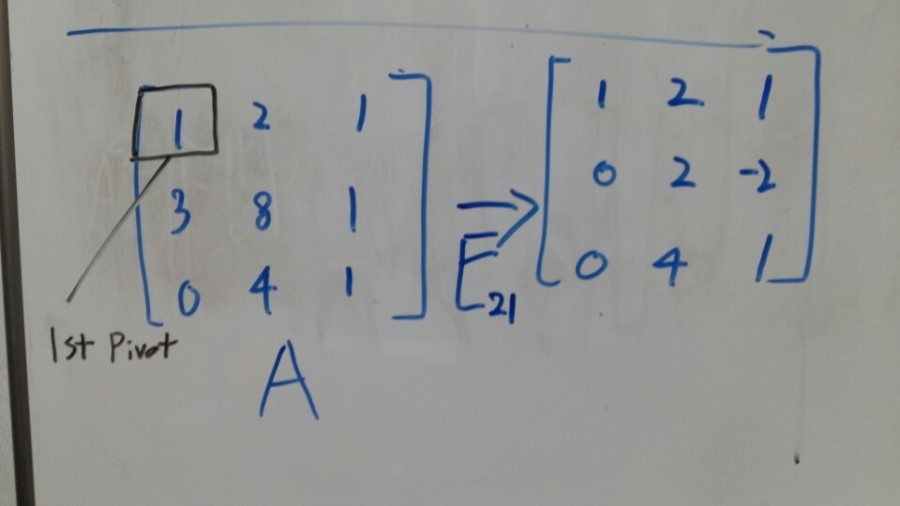
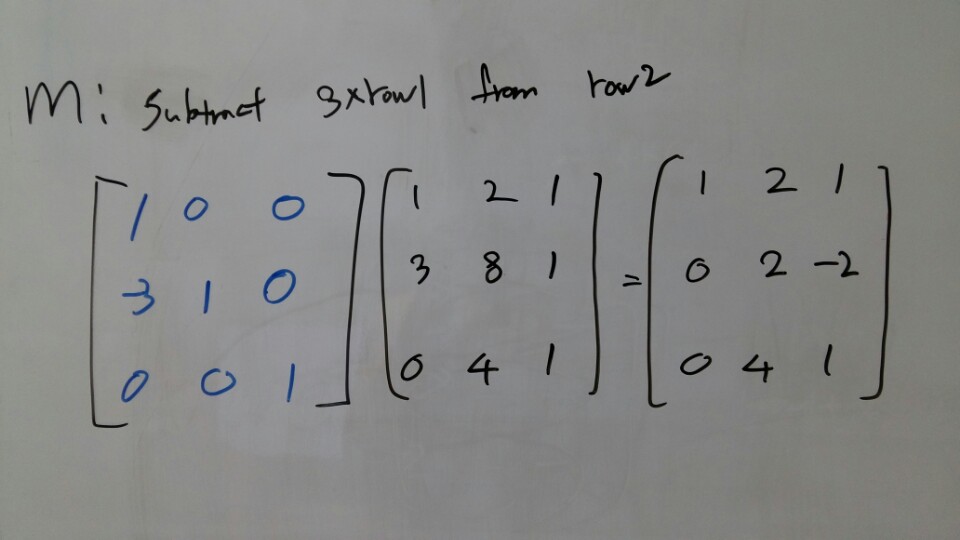
And What’s the multiplier? It’s 3.
3 Times of first equation will knock out the x part of the second equation.
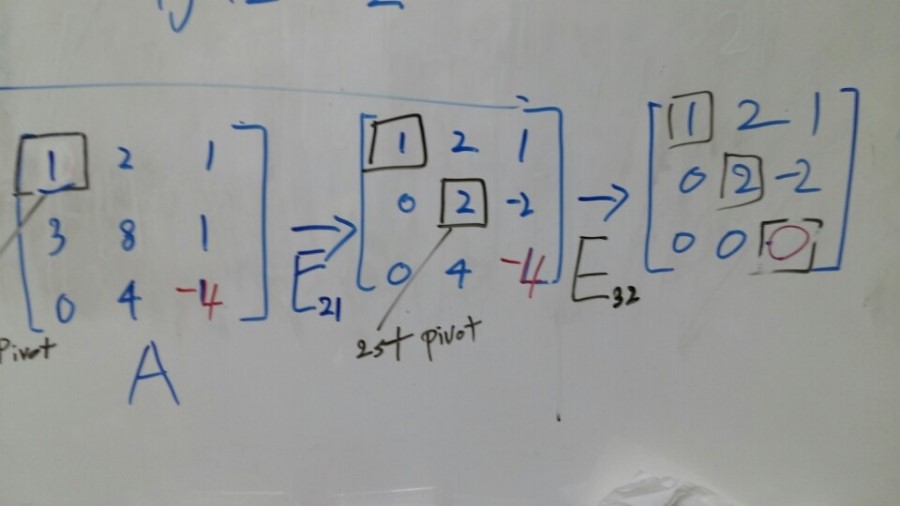
Here’s the result.
[Picture 2]
What we did was just remove the element row 2 column 1 in the matrix.
So I’m going to call this operation E21. E is E of Elimination.
The next thing we have to do is remove the be left x part of the equations. But fortunately other x part has already been 0.
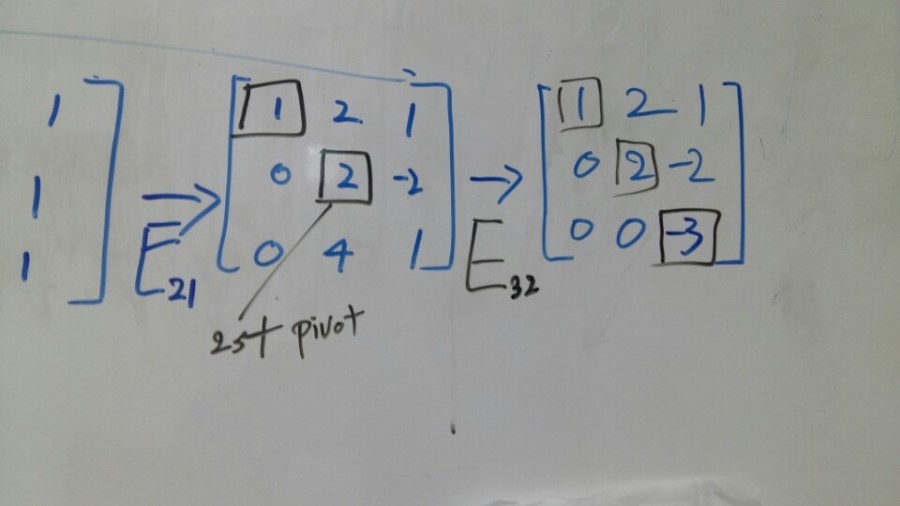
Okay. Now what? Now we can see the second pivot. 2 of second row.
Now It’s the time to remove the y part of the equations.
And the multiplier is 2. Right? We want to remove the 4 part of the third equation.
[Picture 3]
Here’s the result.
And as like before, I’m going to call this operation as E32. Because I’ve removed the row 3 column 2 part of the matrix.
So, we’ve got three pivots. This shape of matrix is called U for Upper triangular.
Now We’ve got ready to solve the equations.
But before starting to solve the problem, Let’s talk about the failure case.
How could I have failed? When I fail to get three pivot then I fail to solve the equations.
Then let’s take an example. What if the there was 0 in first pivot position?
[Picture 4]
In that case, We just can get out of from the trouble by switching the row 1 and row 2. We just can move the zero to other position.
Let’s take an another example. What if row 3 column 3 part is -4?
[Picture 5]
Then we will get the zero at the third pivot position and there’s nothing to replace zero. In that case, we are in trouble.
Now get back to the succeed situations, and Let’s fill the right part of the matrix which I’ve missed.

[Picture 6]
How can I solve the equations from the matrix?
The last thing is a back-substitution.
Let’s move the matrix result as equations.

[Picture 7]
It’s the back-substitution. A simple step solving the equations from the matrix result.
Now I’ve got the matrices for elimination. But I haven’t got the operation for elimination yet.
From now on, Let’s say about the elimination operation.
In the process of elimination, We removed the x part from the rows. Except the pivot. Here’s the first operation that we did.

[Picture 2]
We removed the row 2 column 1 from the matrix by operation E21.
And the operation E21 multiply 3 to the first row and subtract it from row 2.
Then How can I define that operation as a matrix form?
Before go to know this, Let me go over one.
Last time I said that multiplying matrix by a vector is a combination of columns.
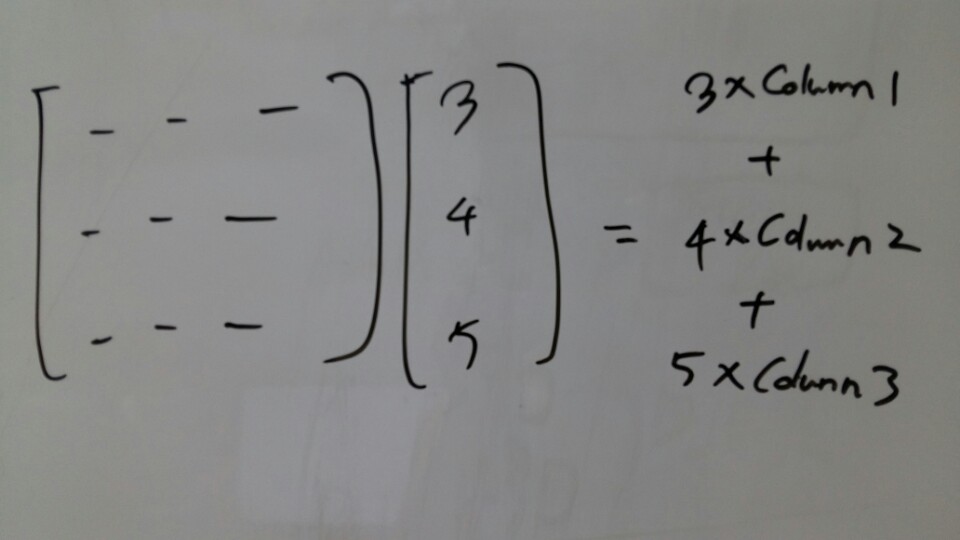
[Picture 8]
It was the column operation. I multiplied some vector to the right side of the matrix.
Then What happen? If I do a row operation. What If I multiply some vector to the left side of the matrix?
Suppose I have some matrix and suppose I multiply the vector (1,2,3) to the left side of matrix.
Then what the result is it?
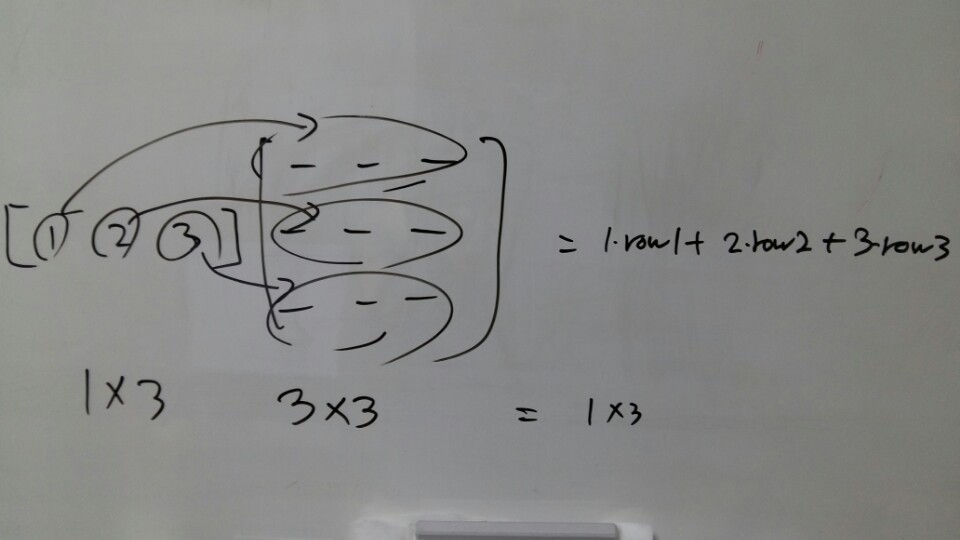
I could say the vector is a 1x3 matrix and the matrix is a 3x3 matrix.
Then the result would be a 1x3 vector. A row vector.
When we multiplied the column vector, we got the column vector.
Likewise If we multiply the row vector, then we get the row vector.
It’s a combination of rows.
[Picture 9]
Okay. I want to use that.
Go back to the E21. What matrix does same work as operation E21 dose?

[Picture 10]
It would be very simple matrix.
The first row of the matrix will be 1 0 0.
Because we want to get 1xRow1 + 0xRow2 + 0xRow3 for row1 of the result matrix.
Likewise the third row of the matrix will be 0 0 1.
Because we don’t want the elements of row 1 and row 2. And we only want the row 3 that is multiplied by 1.
Now the second row of the matrix is quite clear. We want (-3)xrow1 + 1xrow2 + 0xrow3.
So, the second row of the matrix will be -3 1 0.
[Picture 11]
Now we’ve got the first matrix of elimination operation. In the same way we can get the second matrix of elimination operation.

[Picture 12]
Now I’ve got the every matrix of elimination steps.
For next, I will express everything what I did in the post.
Start from the matrix A, I’ve multiplied E21 and E32 and got the result matrix U.
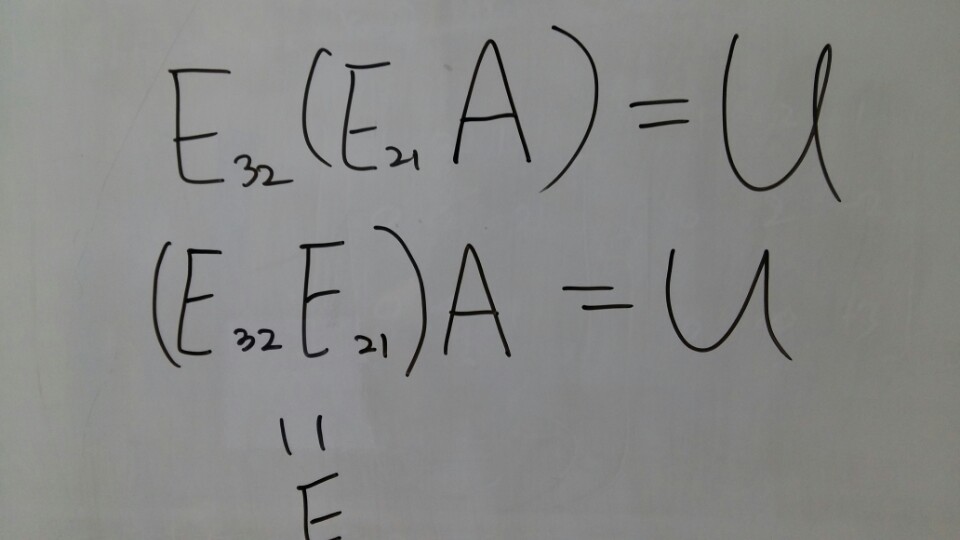
[Picture 13]
And here’s the thing.
What matrix can do the whole job that E21 and E32 did?
It’s the E32E21.
In every matrix multiplication, you can move the parentheses. It is called the associative law.
Now you’ve known how to do matrix elimination and how to make an elimination operation matrix.
But I forgot the something. The permutation matrix.
Let’s think the case that I have to exchagne rows 1 and 2 of matrix.
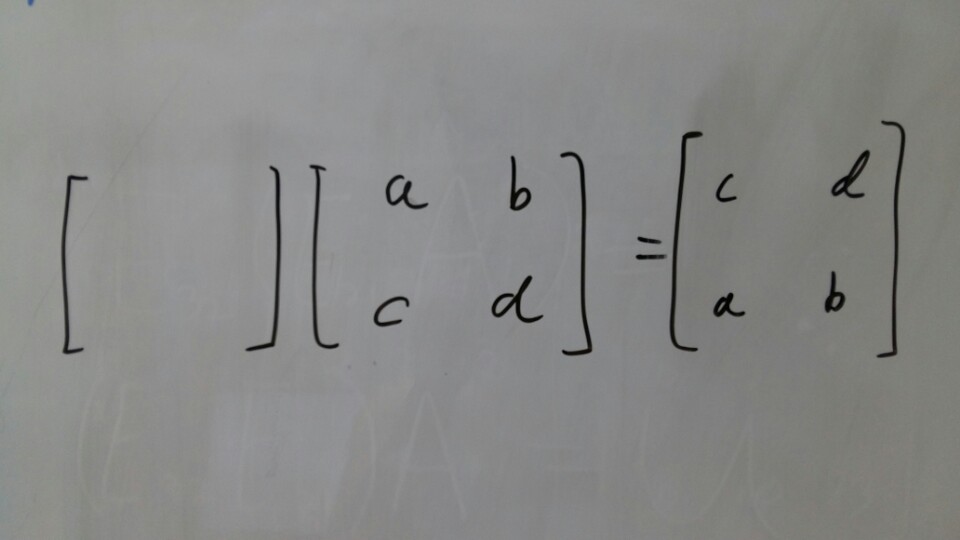
[Picture 14]
What is the matrix for this?
For the first row of the result, I want c d.
I could get c d by multiply row1 and zero, And row2 and one.
This is the permutation matrix.
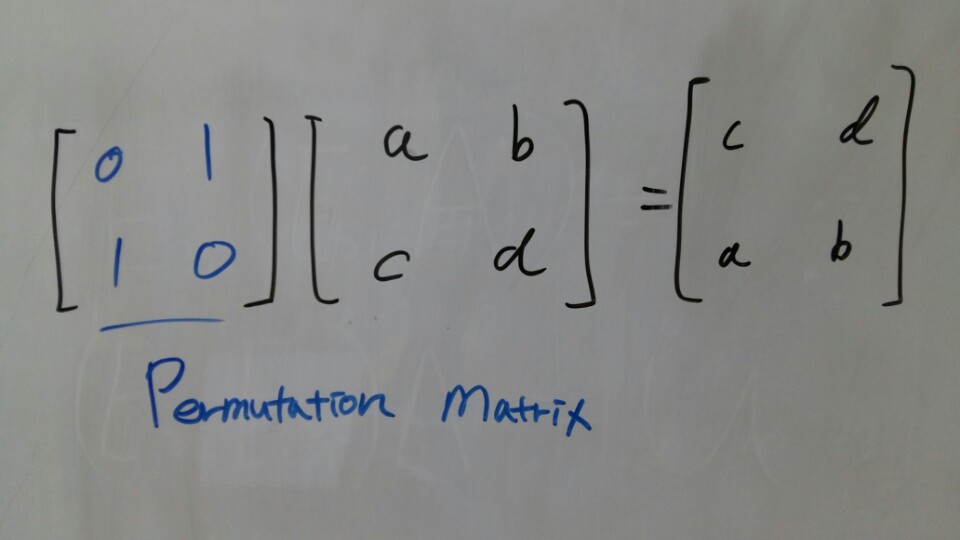
[Picture 15]
Then What if I want to exchange the columns? How would I do that?
We did the row exchanges by multiplying row vectors.
likewise we can exchange the columns by multiplying column vectors.
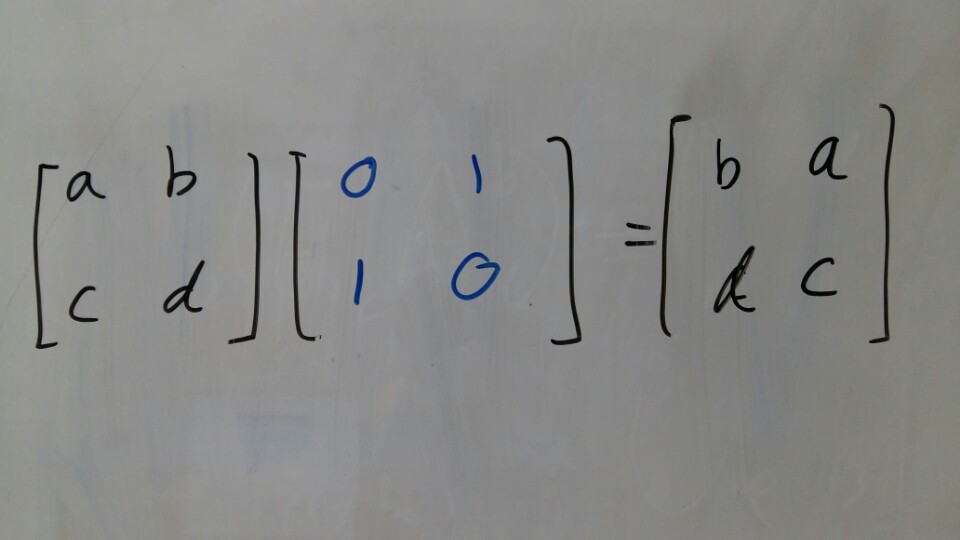
[Picture 16]
Now the explainations about the matrix elimination is done.
But before to end up the post, here’s the intereting thing.
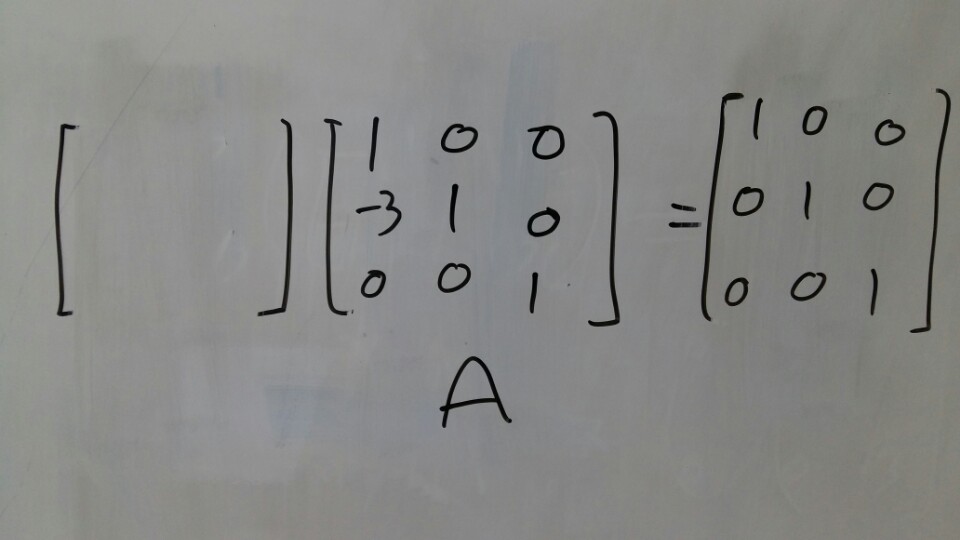
You can get the inverse matrix from the what I did today.
The inverse matrix is the matrix that makes the other matrix to identity matrix. Let’s take an example.
[Picture 17]
What matrix makes the A as identity matrix?
We already have been through this step from the matrix elimination steps.
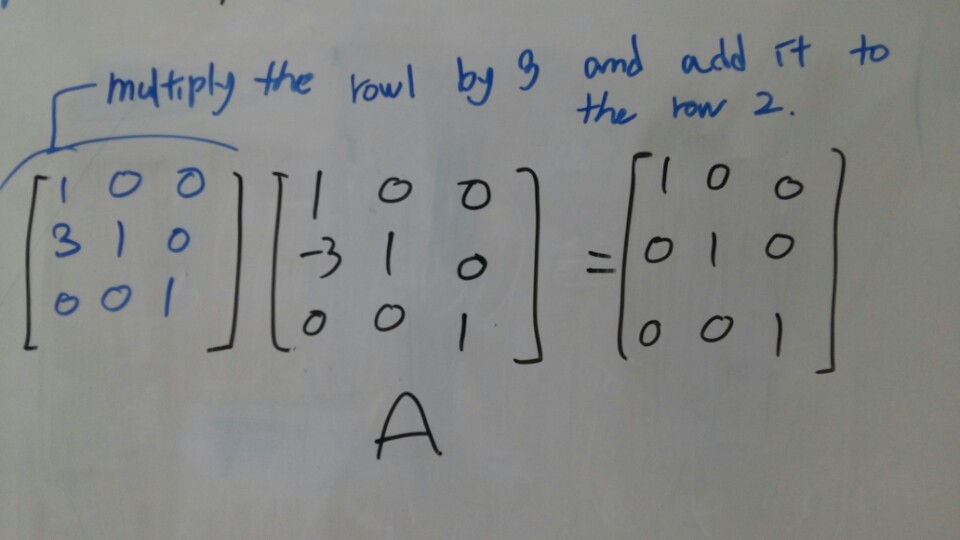
[Picture 18]
Now this post is ended. See you next time!
Reference: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZK3O402wf1c&list=PLE7DDD91010BC51F8